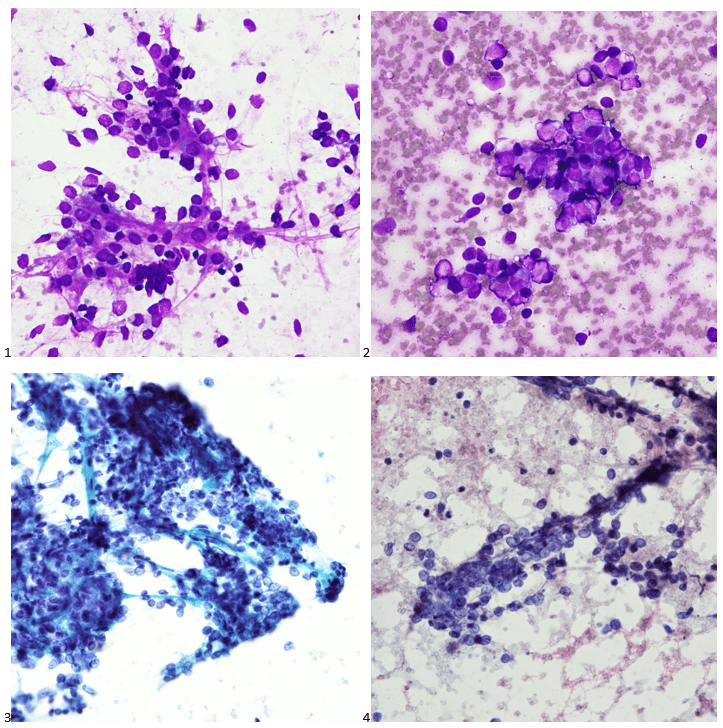
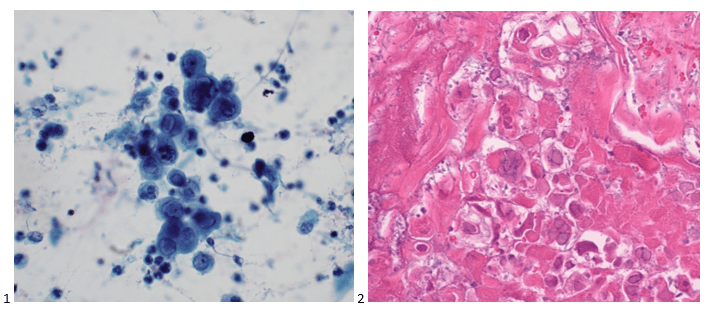
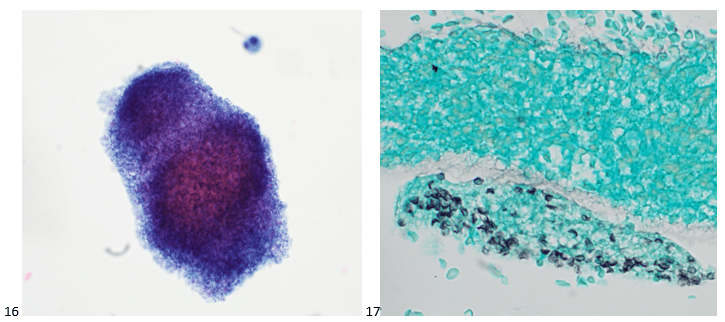
Back in the olden days – wait, can I use that line yet? I graduated from my cytology program ten years ago, which feels like two decades ago or just yesterday. Depends on the day. Anyway, there are little nuggets from my training that stick with me whenever I’m screening a case. This case revolves around the concept of a two-cell population in body fluids, namely pleural, peritoneal, and pericardial. We were taught that if you see a two-cell population, the case is malignant. I remember asking in school, “But what if the diagnosis is mesothelioma?” “Okay,” my professor said, “that applies to any malignancy except mesothelioma. The two-cell population indicates a population of benign mesothelial cells and a second population of malignant cells.” Noted! I live by this rule, and every now and then, I have a case of a peritoneal fluid where the slides are covered in “wall-to-wall” adenocarcinoma, and I can’t find a benign mesothelial cell for the life of me. Obviously, we let years of experience with morphology take the reins there, but there are still those cases where the native mesothelial cells are so reactive in appearance that we start hunting for a two-cell population. This case was a perfect blend of wall-to-wall tumor and more-than-reactive mesothelials.
When a patient is being worked up for the first time or the nth time, we recognize their names and recall their clinical history and previous morphologies. Quite often we have patients with genetic predispositions to cancer who present with one type of cancer and are treated accordingly, and during surveillance imaging, come back to us with a second primary cancer. In this case, we received a right-sided pleural fluid on a 73-year-old woman with a history of ER+/PR+/HER2- breast cancer. After a history of incomplete medical follow-up, the patient presented to a local emergency room with pleuritic pain, upon which a CT Scan identified a lung mass, breast mass, and multiple liver and upper thoracic bone lesions. The assumption, given the clinical history, was metastatic breast cancer, and the clinician submitted the pleural fluid for cytology to repeat ER/PR/HER2 testing to determine if there is a better treatment strategy than her current aromatase inhibitor, which appeared to be failing.
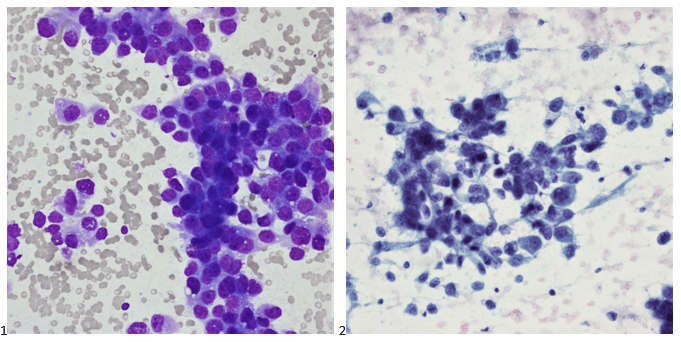
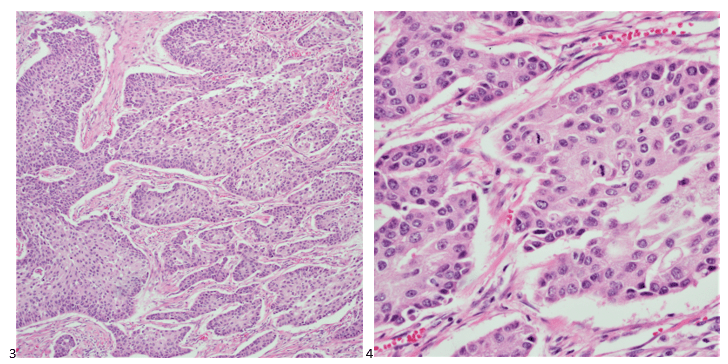
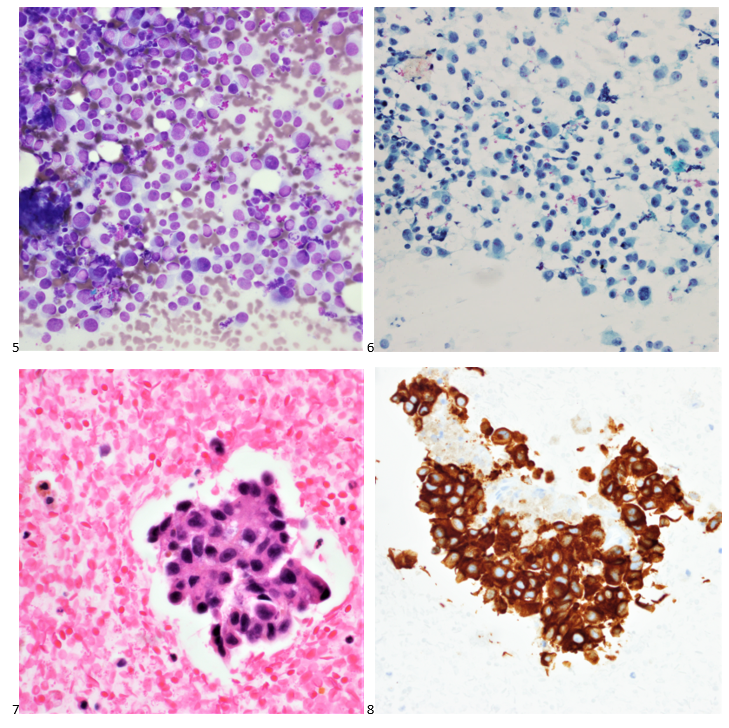
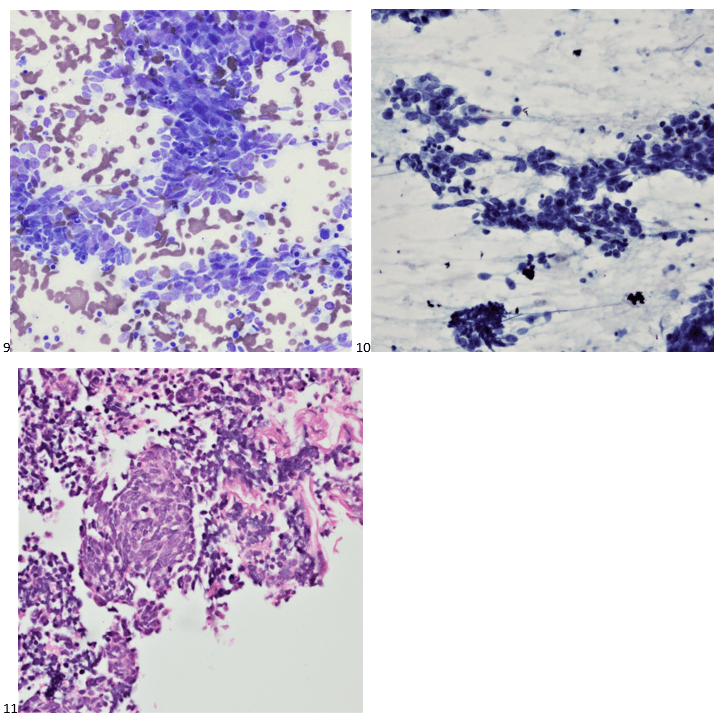
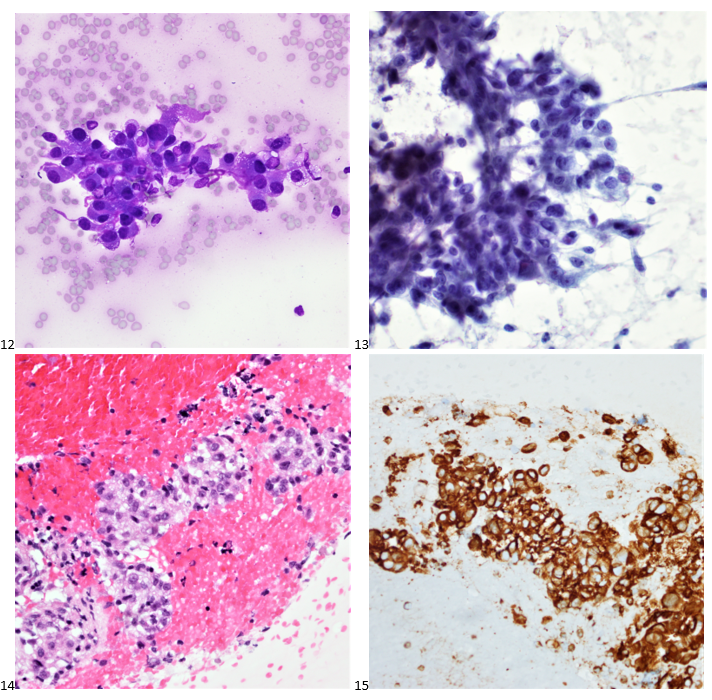
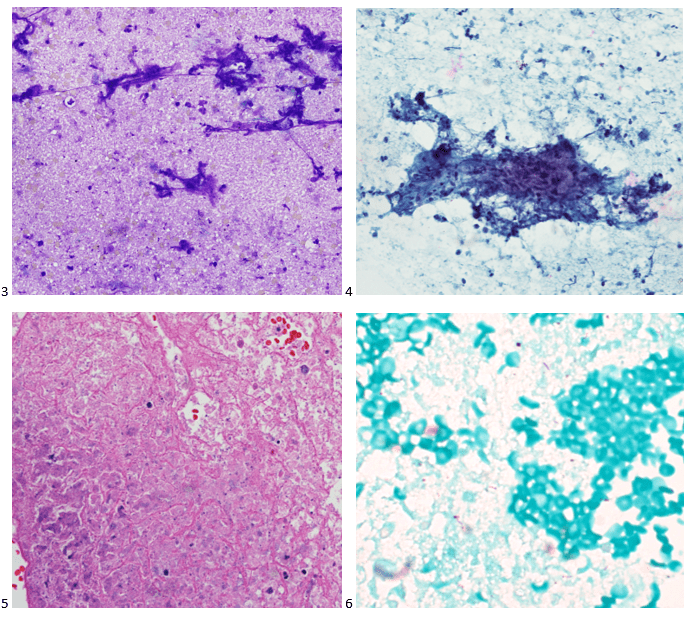
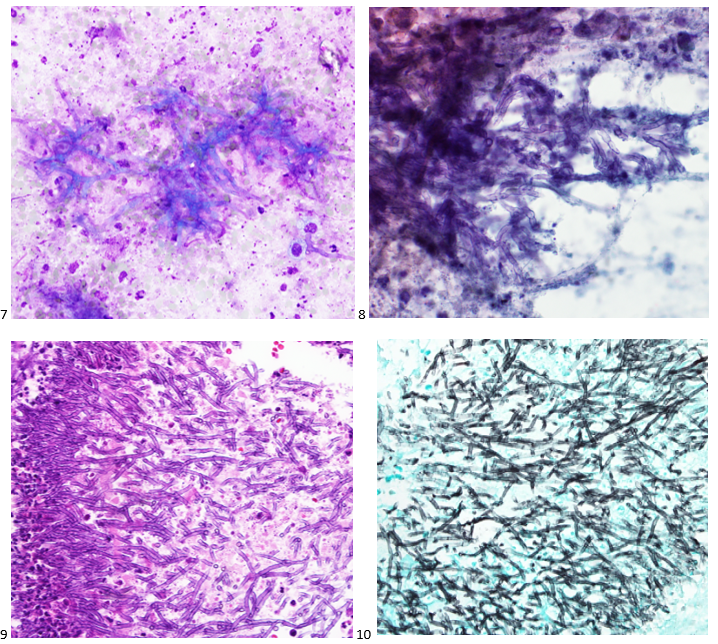
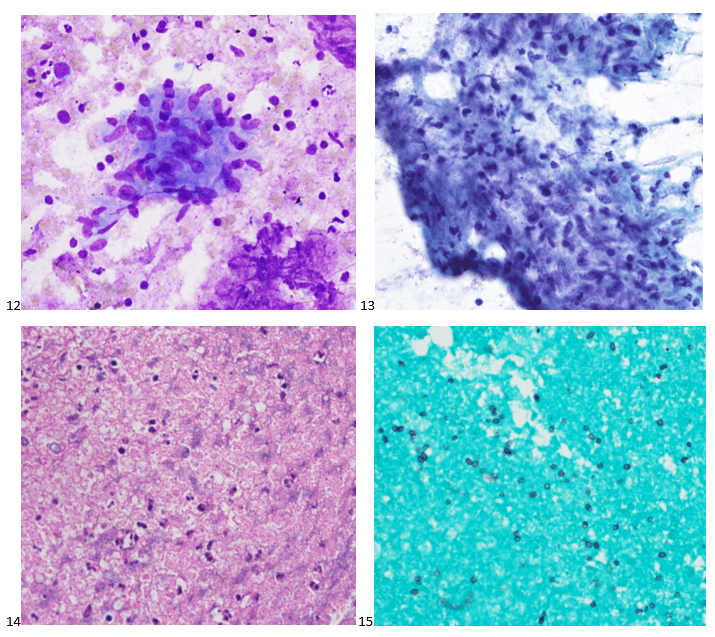
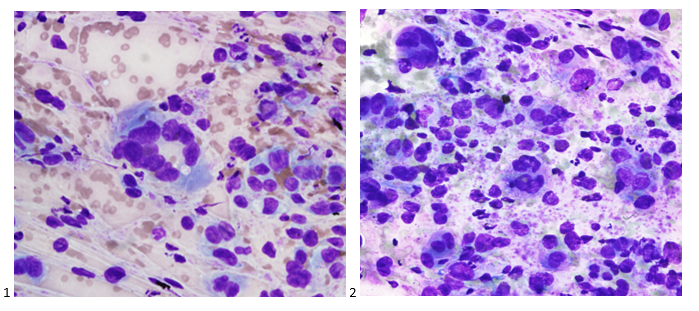
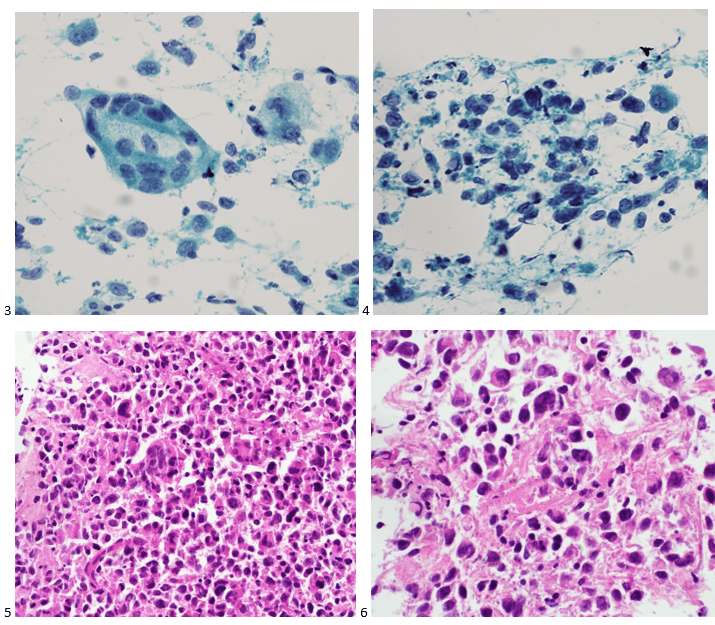
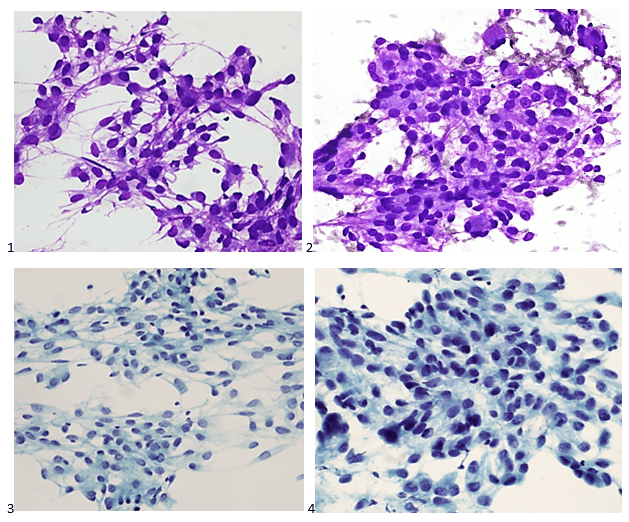
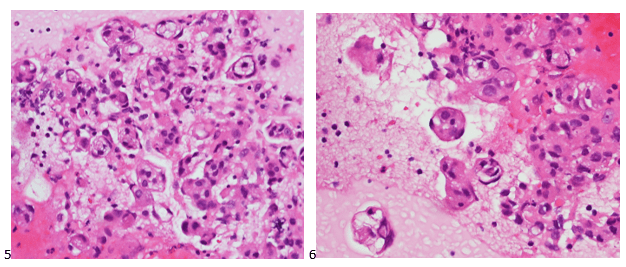
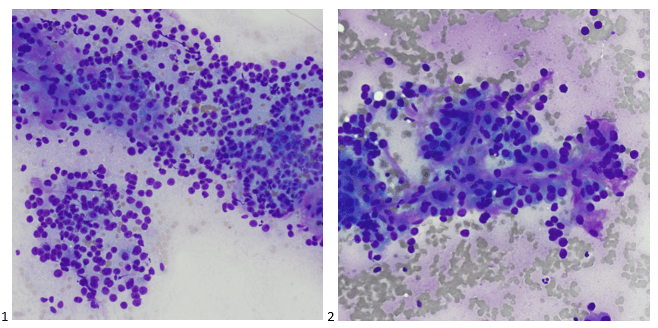
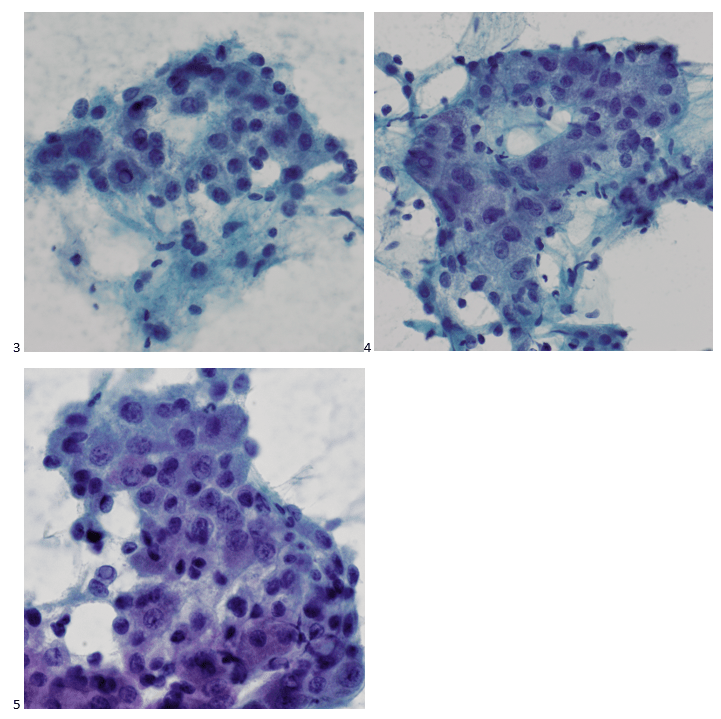
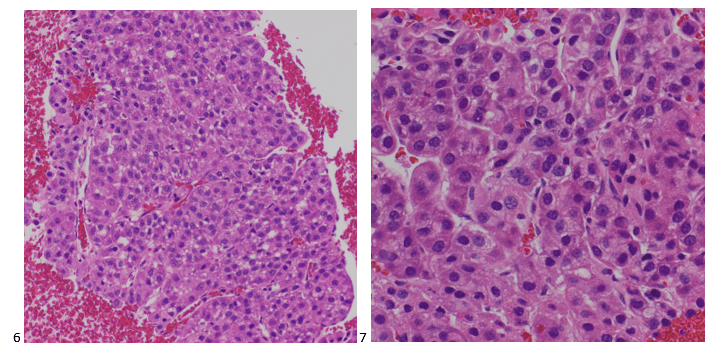
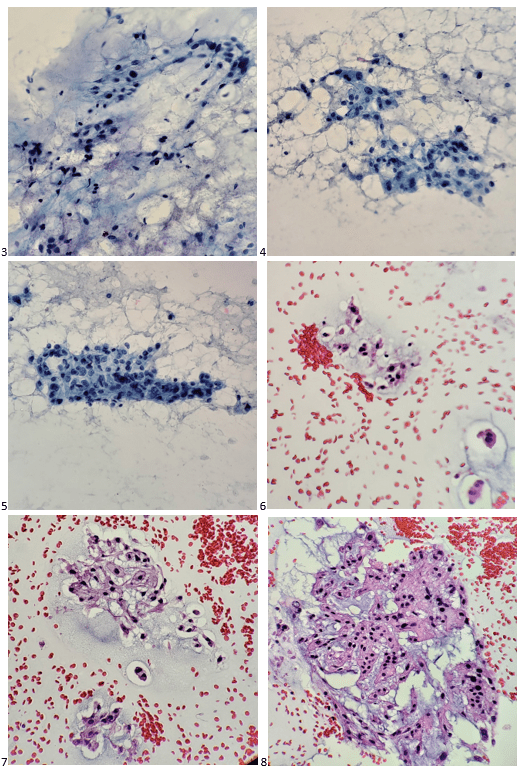
Upon screening the cytopreparations, we observed very obvious malignant cells (Image 1). It was evident that we had a two-cell population. One of the cell populations was characterized by cohesive clusters of relatively uniform tumor cells (Image 2 & 4) and the second cell population was less cohesive with larger pleomorphic cells (Image 3 & 4). Hmm, something doesn’t make sense here. We already have a group of tumor; the other cells are supposed to be benign mesothelials cells. Is there a mixed morphology going on? Like a combined small cell carcinoma and non-small cell carcinoma that we might see in lung cancer? It’s not small cell though. These two populations are clearly two adenocarcinomas. That still can’t be. There has to be a population of mesothelials. No, no… the benign mesothelials are scattered throughout the background. It looks like a double-malignant three-cell population!
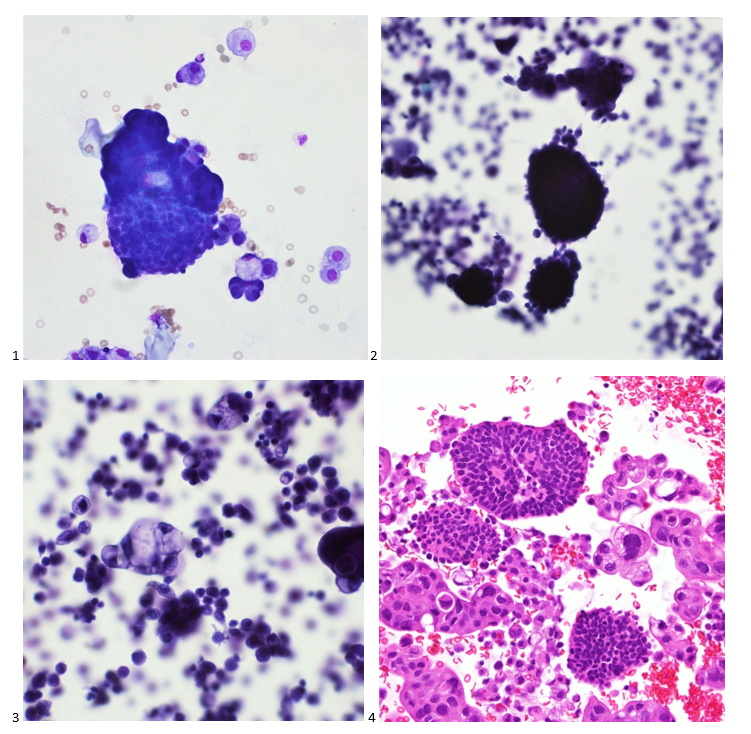
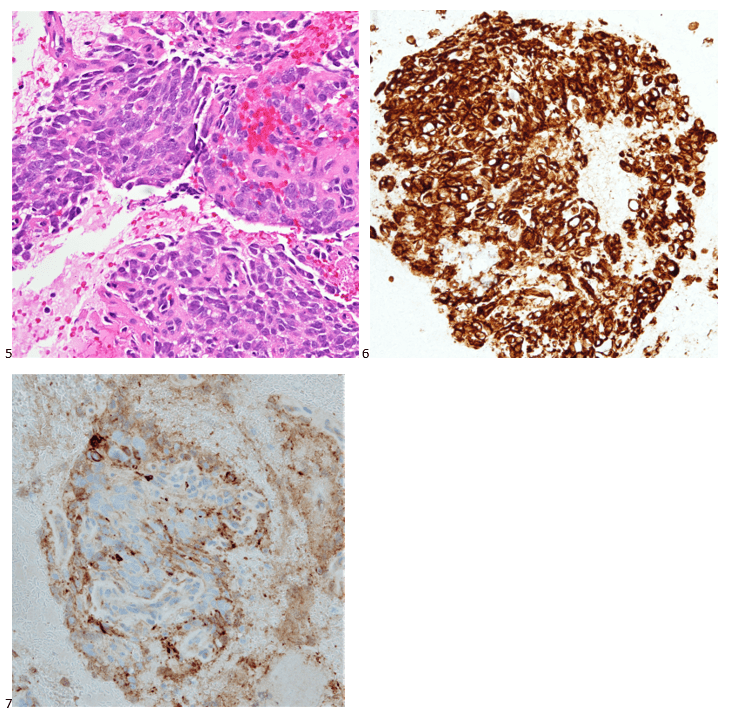
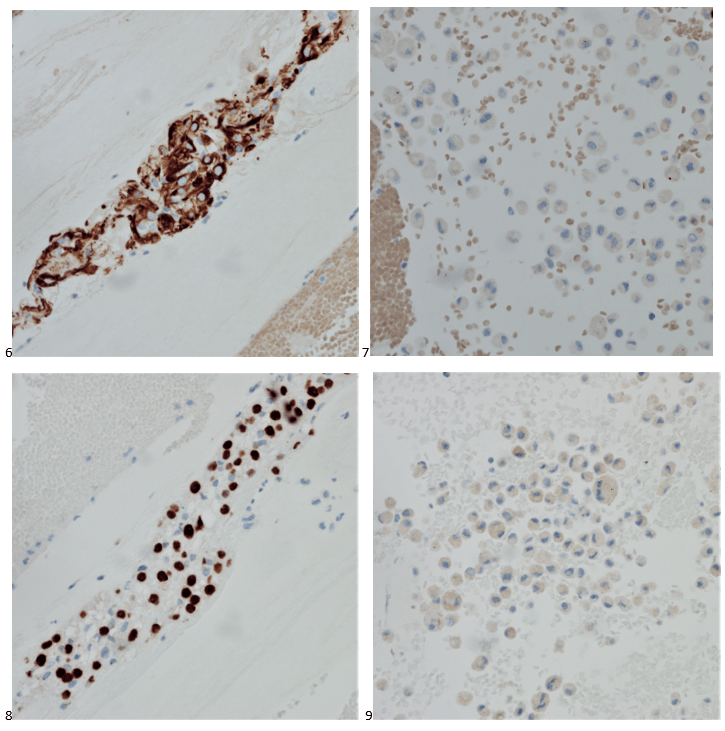
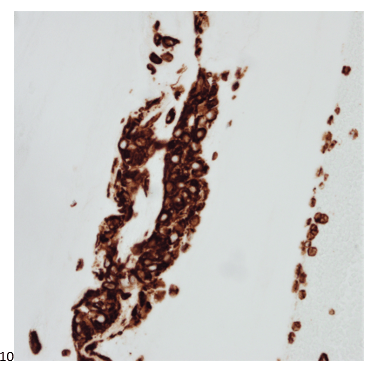
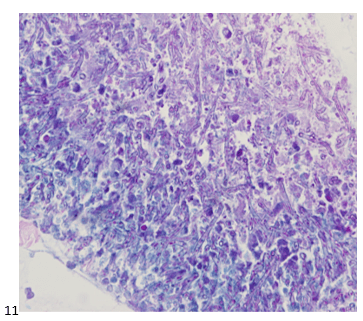
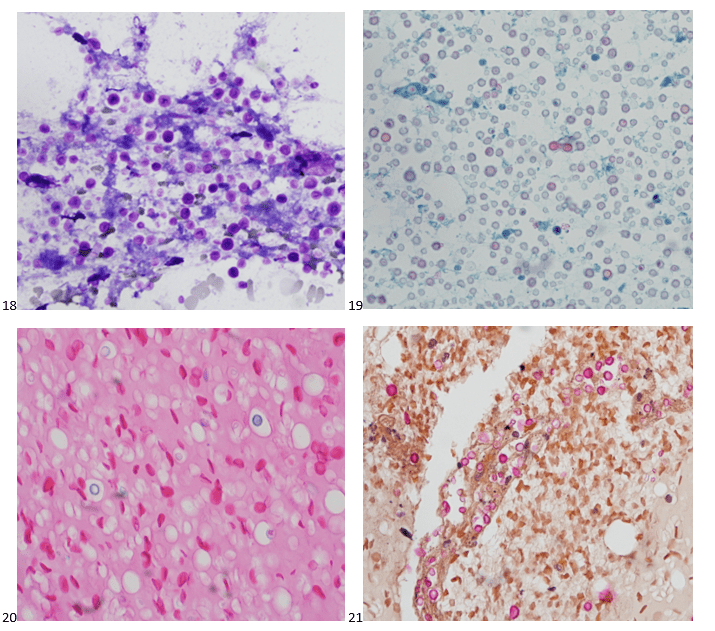
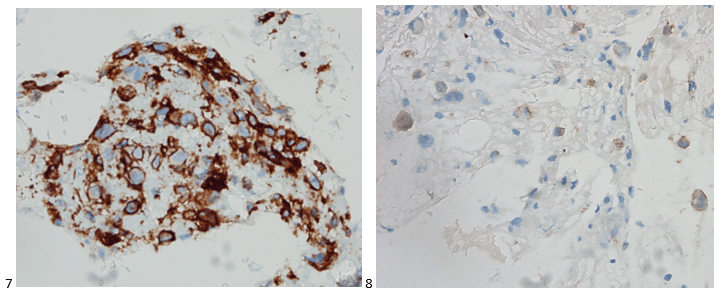
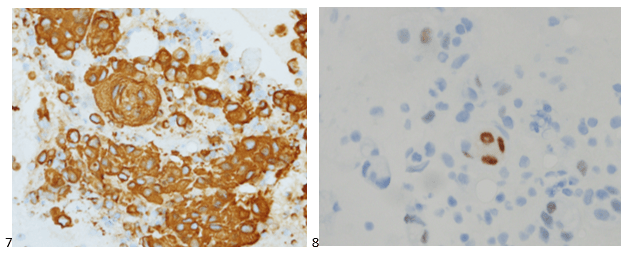
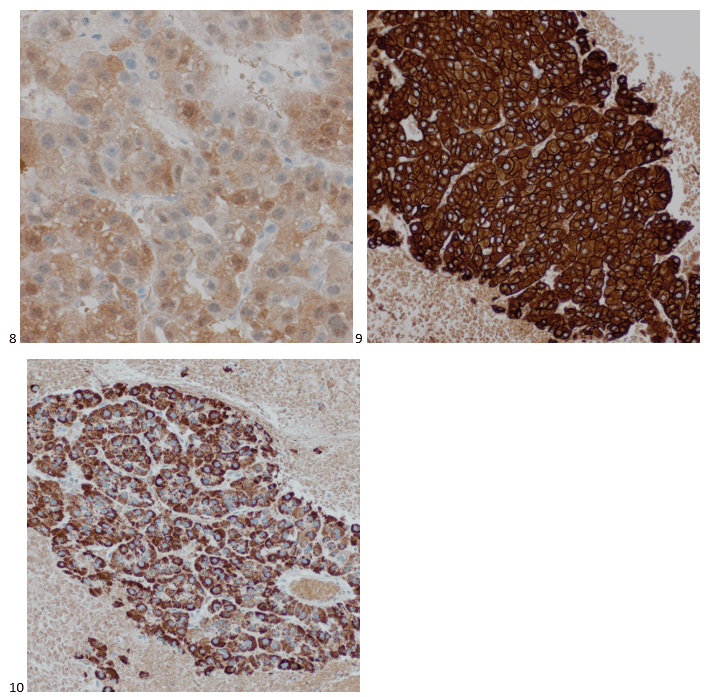
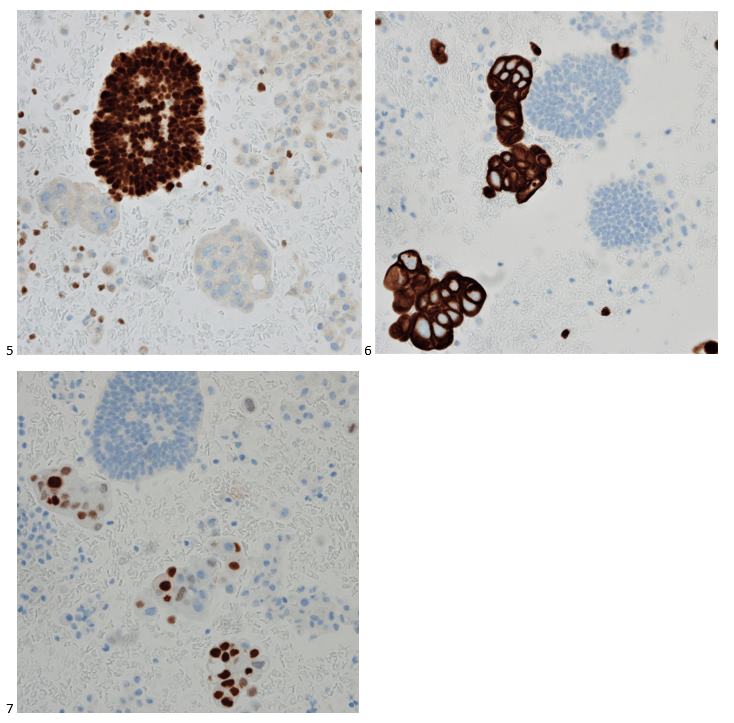
We submitted the case to the cytopathologist on service for the day. When they asked what we had, we replied, “All the adenocarcinoma,” and noted that we definitely need ER/PR/HER2 as clinically and now morphologically, it appears that the patient’s breast cancer is involving the pleural fluid. The cytopathologist agreed that there was something to the case. Metastatic breast cancer likes to appear as cannon balls in fluid (Image 2), the second cell population is too unlike the first. The cytopathologist performed immunocytochemical stains on paraffin sections of the cell block with adequate controls. The first type of cells shows positive staining for CK7, CK19, GATA3 (Image 5), and ER, and negative staining for CK20 (Image 6), CDX-2 (Image 7), BRST2, and PR. The second type of tumor cells show positive staining for CK7, CK20 (Image 6), CK19, and CDX-2 (Image 7), and negative staining for GATA3 (Image 5), ER, PR, and BRST2. The former group of cells has a morphology and immunoprofile consistent with breast origin, and the latter group of cells are morphologically and immunophenotypically suggestive of a pancreaticobiliary or gastrointestinal tract origin.
Final Diagnosis: Positive for malignancy. Adenocarcinoma, consistent with metastatic breast and metastatic pancreaticobiliary or gastrointestinal tract origin.
Interestingly, the patient had a paracentesis and liver biopsy the following week, and only the pancreaticobiliary or GI tract origin immunoprofile was positive in the peritoneal fluid and FNA. The patient’s breast cancer seemed to remain above the diaphragm.

-Taryn Waraksa-Deutsch, DHSc, SCT(ASCP)CM, CMIAC, LSSGB, is the Cytopathology Supervisor at Fox Chase Cancer Center, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She earned her master’s degree from Thomas Jefferson University in 2014 and completed her Doctorate of Health Science from Bay Path University in 2023. Her research interests include change management and continuous improvement methodologies in laboratory medicine. She is an ASCP board-certified Specialist in Cytology with an additional certification by the International Academy of Cytology (IAC). She is also a 2020 ASCP 40 Under Forty Honoree. Outside of her work, Taryn is a certified Divemaster. Scuba diving in freshwater caverns is her favorite way to rest her eyes from the microscope.